During a Redox Reaction the Oxidation Numbers of Oxidizing Agents
In the above redox reaction. This species is often referred to as the reducing agent.

Oxidation Number Example 3 Redox Reactions Oxidation Chemistry
Is it a Redox Reaction.

. During a redox reaction oxidation numbers change. Compare the oxidation numbers from the reactant side to the product side. In a redox reaction there is always an oxidizing and reducing agent NO_3- is most likely to be a strong oxidizing agent.
Boric acid BOH 3 is a Tribasic acid. The species getting reduced is called the oxidizing agent. Common examples of oxidizing agents include halogens such as chlorine and fluorine oxygen and hydrogen peroxide H 2 O 2.
Any reaction in which the change of oxidation state of any of the element changes with respect to the lhr and rhr the reaction is said to be a redox reaction. Check the oxidation numbers. An oxidizing agent is thus an electron acceptor.
If the oxidation number is greater in the product then it lost electrons and the substance was oxidized. SO4 The oxidation number of Chromium in Na2Cr2O7. In all compounds the sum of all oxidation numbers must equal _____ 0.
NH_3 is most likely to be a strong reducing agent. An oxidizing agent is a reactant that removes electrons from other reactants during a redox reaction. Click to see full answer.
Cause an increase in the oxidation state of the substance by making it lose electrons. In redox reactions H 2 O 2 may behave as oxidizing as well as reducing agent depending upon the other reactants. Reducing agent becomes reduced.
Because the oxidizing agent is gaining electrons and is thus often called an electron acceptor it is said to have been reduced. Here C is oxidised to CO because oxygen is being added and ZnO is reduced to Zn because oxygen is being removed. So to identify an oxidizing agent simply look at the oxidation number of an atom before and after the reaction.
In most cases the oxidizing. Oxidizing agents cause the other compounds oxidation number to increase ex. Use oxidation numbers to identify the element oxidized the element reduced the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent.
H2O and O2 respectively-1-20. Redox shorthand for reductionoxidation reaction describes all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation number oxidation state changed. When an atom gains electrons.
Use oxidation numbers to identify the element oxidized the element reduced the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent. In which process does a substance act as both an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent and oxidizes itself. This may be a little confusing at first but remember the oxidizing agent is the species that causes another to become oxidizedsince redox reactions happen in pairs of reduction and oxidation the species causing oxidation is the one getting reduced.
In redox reactions The species that loses electrons is oxidized. The oxidizing agent typically takes these electrons for itself thus gaining electrons and being reduced. The reaction is a redox process.
MnO 4 has been reduced by SO 2 and so SO 2 is the reducing agent. During redox reactions reducing agents. Going from a 2 to a 3 or from a -2 to a -1 while reducing agents cause the other compounds oxidation number to.
The species that is reduced causes something else to be oxidized. If the oxidation number is less then it gained electrons and was reduced. The species that increases in oxidation number.
During a redox reaction the reducing agent reduces the oxidizing agent. This is determined by comparing the oxidation numbers of nitrogen. The oxidation number of any uncombined element The oxidation numbers of the atoms in any polyatomic ions should be equal to this The oxidation number of Sulfur in a Sulfate Ion.
The reaction in which one substance gets oxidised and other gets reduced is known as redox reaction. In H 2 O 2 oxygen is in -1 oxidation state which may be increased to zero or decreased to 2. ZnO C Zn CO.
The reducing agent has the electrons at the start of the redox reaction while the oxidizing agent has the electrons after the reaction is completed. The one whose oxidation number decreases during the redox process is the oxidizing agent. The species that gains electrons is reduced.
The answer is C. In the above redox reaction. Does it gain or lose electrons.
The species that decreases in oxidation number. Oxidizing agents are also known as oxidants or oxidizers. In the case of a.
This species is often referred to as the oxidizing agent. An oxidizing agent often referred to as an oxidizer or an oxidant is a chemical species that tends to oxidize other substances ie. An oxidizing agent is the element or compound in an oxidation-reduction redox reaction that accepts an electron from another species.
- both use redox reactions - anode- oxidation - cathode- reduction - Electrons flow from anode to cathode. What happens to an oxidizing agent during a redox reaction. What happens to a reducing agent during a redox reaction.
The algebraic sum of the oxidation numbers of the atoms in a neutral compound. 15 Circle the one statement that is false. This can be either a simple redox process such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane CH 4 or it can be a complex process such as the oxidation of.
Here the oxidation state of Mn changes from 4 to 2 while here reduction occursthe oxidation state of Cl changes from -1 to 0 here oxidation occurs. SO 2 has been oxidized by MnO 4 and so MnO 4 is the oxidizing agent. 2MnO_4- 5H_2SO_3 rarr Mn2 5SO_42-.
The only atoms which change are Mn from 7 to 2 a reduction and S from 4 to 6 an oxidation.

อน ม ลอ สระ เคร องทำน ำด าง Enagic Kangenthai Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Lessons

Electrochemistry Playlist Best Chemistry Videos Class 12 Digital Kemistry Youtube Electrochemistry Redox Reactions Chemistry Lessons
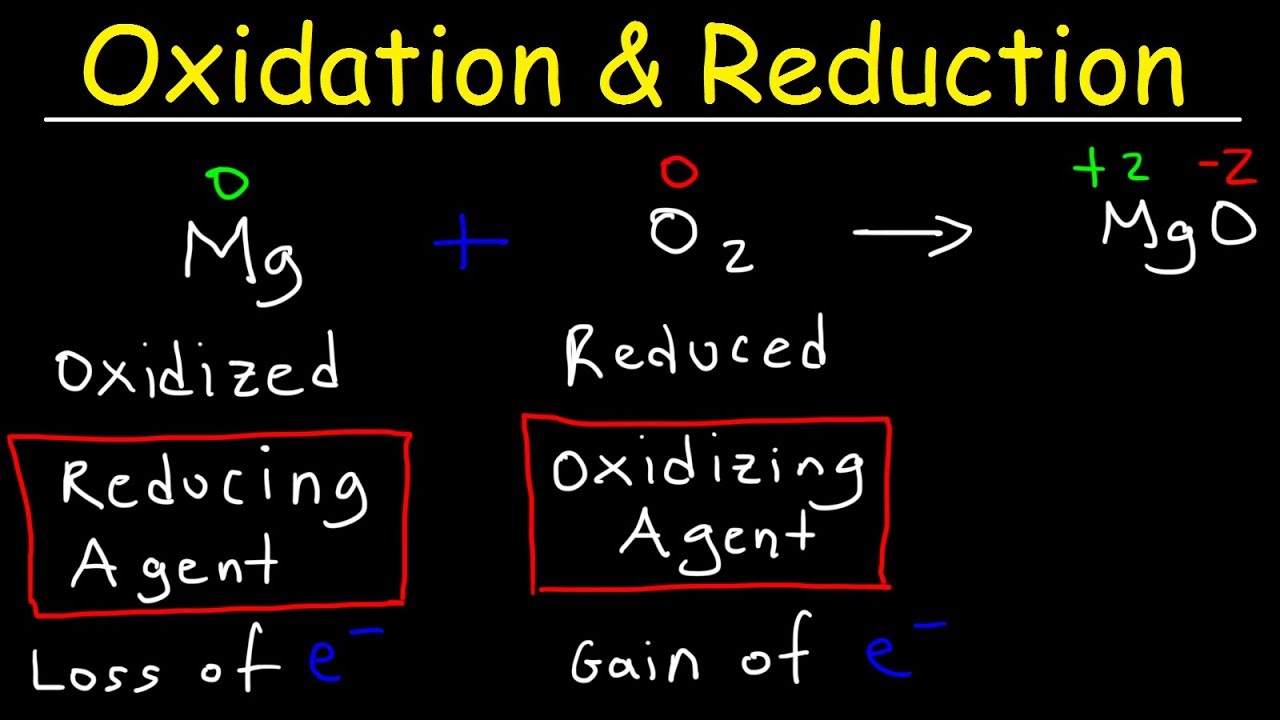
Oxidation And Reduction Redox Reactions And Electrochemistry Chemistry Khan Academy Youtube Chemistry Basics College Chemistry Redox Reactions
Comments
Post a Comment